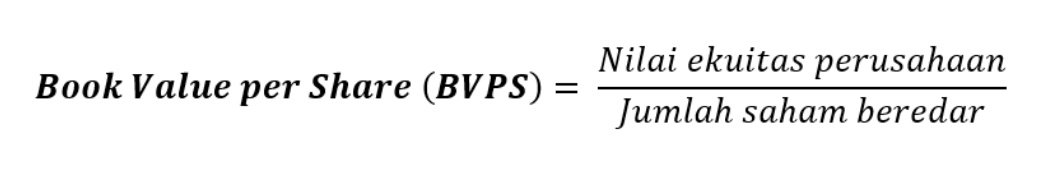
When the market value of a company is less than its book value, it may mean that investors have lost confidence in the company. In other words, the market may not believe the company is worth the value on its books or that there are enough future earnings. If the company is going through a period of cyclical losses, it may not have positive trailing earnings or operating cash flows. Therefore, an alternative to the P/E approach may be used to assess the current value of the stock.
Book Value Greater Than Market Value
In this case, the company’s price/BVPS multiple seems to have been sliding for several years. In this case, the stock seems to trade at a multiple that is roughly in line with its peers. Even though book value per share isn’t perfect, it’s still a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments. Critics of book value are quick to point out that finding genuine book value plays has become difficult in the heavily-analyzed U.S. stock market. Oddly enough, this has been a constant refrain heard since the 1950s, yet value investors continue to find book value plays.
Book Value vs. Market Value: What’s the Difference?
If you are going to invest based on book value, you have to find out the real state of those assets. On the other hand, if a company with outdated equipment has consistently put off repairs, those repairs will eat into profits at some future date. This tells you something about book value as well as the character of the company and its management. You won’t get this information from the P/B ratio, but it is one of the main benefits of digging into the book value numbers and is well worth the time.
Book Value Equals Market Value
Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business. If the company’s BVPS increases, investors may consider the stock more valuable, and the stock’s price may increase. On the other hand, a declining book value per share could indicate that the stock’s price may decline, and some investors might consider that a signal to sell the stock. BVPS is typically calculated quarterly or annually, coinciding with the company’s financial reporting periods. Calculate BVPS for any stocks you own, and you’ll see it can be wildly different from the company’s share price.

What Is Book Value Per Common Share?
Using the same share basis formula, we can calculate the book value per share of Company B. Book Value Per Share also theoretically reflects what shareholders would receive in a company liquidation after all its assets were sold and all of its liabilities paid. However, because assets would hypothetically sell at market value instead of historical asset values, this may not be an entirely accurate measurement. While BVPS considers the residual equity per-share for a company’s stock, net asset value, or NAV, is a per-share value calculated for a mutual fund or an exchange-traded fund, or ETF. For any of these investments, the NAV is calculated by dividing the total value of all the fund’s securities by the total number of outstanding fund shares.
If the market price for a share is higher than the BVPS, then the stock may be seen as overvalued. A negative book value means that a company’s liabilities are greater than its assets. On the other hand, value investors might look for a company where the market revzilla promo code reddit march 2021 value is less than its book value hoping that the market is wrong in its valuation. Making Calculations Practical Now it’s time to use the calculation for something. The first thing one might do is compare the price/BVPS number to the historic trend.
- Now, let’s say that the company invests in a new piece of equipment that costs $500,000.
- The term “book value” is derived from accounting lingo, where the accounting journal and ledger are known as a company’s books.
- If a company is selling 15% below book value, but it takes several years for the price to catch up, then you might have been better off with a 5% bond.
- If, for example, the company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, common equity increases along with BVPS.
- The examples given above should make it clear that book and market values are very different.
If the company has been depreciating its assets, investors might need several years of financial statements to understand its impact. Additionally, depreciation-linked rules and accounting practices can create other issues. For instance, a company may have to report an overly high value for some of its equipment.
However, if advertising efforts enhance the image of a company’s products, the company can charge premium prices and create brand value. Market demand may increase the stock price, which results in a large divergence between the market and book values per share. Should the company dissolve, the book value per common share indicates the dollar value remaining for common shareholders after all assets are liquidated and all creditors are paid. If the book value is based largely on equipment, rather than something that doesn’t rapidly depreciate (oil, land, etc.), it’s vital that you look beyond the ratio and into the components.
Enterprise value, or firm value, market value, market capitalization, and other methods may be used in different circumstances or compared to one another for contrast. For example, enterprise value would look at the market value of the company’s equity plus its debt, whereas book value per share only looks at the equity on the balance sheet. Conceptually, book value per share is similar to net worth, meaning it is assets minus debt, and may be looked at as though what would occur if operations were to cease. One must consider that the balance sheet may not reflect with certain accuracy, what would actually occur if a company did sell all of their assets.
BVPS is what shareholders receive if the firm is liquidated, all tangible assets are sold, and all liabilities are paid. The good news is that the number is clearly stated and usually does not need to be adjusted for analytical purposes. As long as the accountants have done a good job (and the company’s executives aren’t crooked) we can use the common equity measure for our analytical purposes. The book value of a company is based on the amount of money that shareholders would get if liabilities were paid off and assets were liquidated. The market value of a company is based on the current stock market price and how many shares are outstanding. Book value per share (BVPS) tells investors the book value of a firm on a per-share basis.
Carrying value is the asset’s original cost less any accumulated depreciation or amortization. Accumulated depreciation is the aggregate depreciation recorded against that asset during its lifetime. In theory, a low price-to-book-value ratio means you have a cushion against poor performance. Outdated equipment may still add to book value, whereas appreciation in property may not be included.

No comment